Faster Delivery in 3-5 Days
Faster Delivery in 3-5 Days

Some car components are only remembered when they stop working. And when those parts are expensive to repair or replace, you might even "bless" their inventor out of frustration. One of the best examples in modern vehicles is the EGR valve.
Do you really know what it is, how it works, or how it fails? In this guide, we break it all down—and show how tools like Autel diagnostic scanners can help.
Take a look at the component in the image below. The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve has been a legally mandated part of most vehicles since the introduction of Euro 2 emissions standards in 1996. Its job? To help reduce the level of harmful pollutants emitted from internal combustion engines—especially nitrogen oxides (NOx).
Like every component, it must work properly to be effective. And when it doesn’t, your engine and emissions system can suffer.
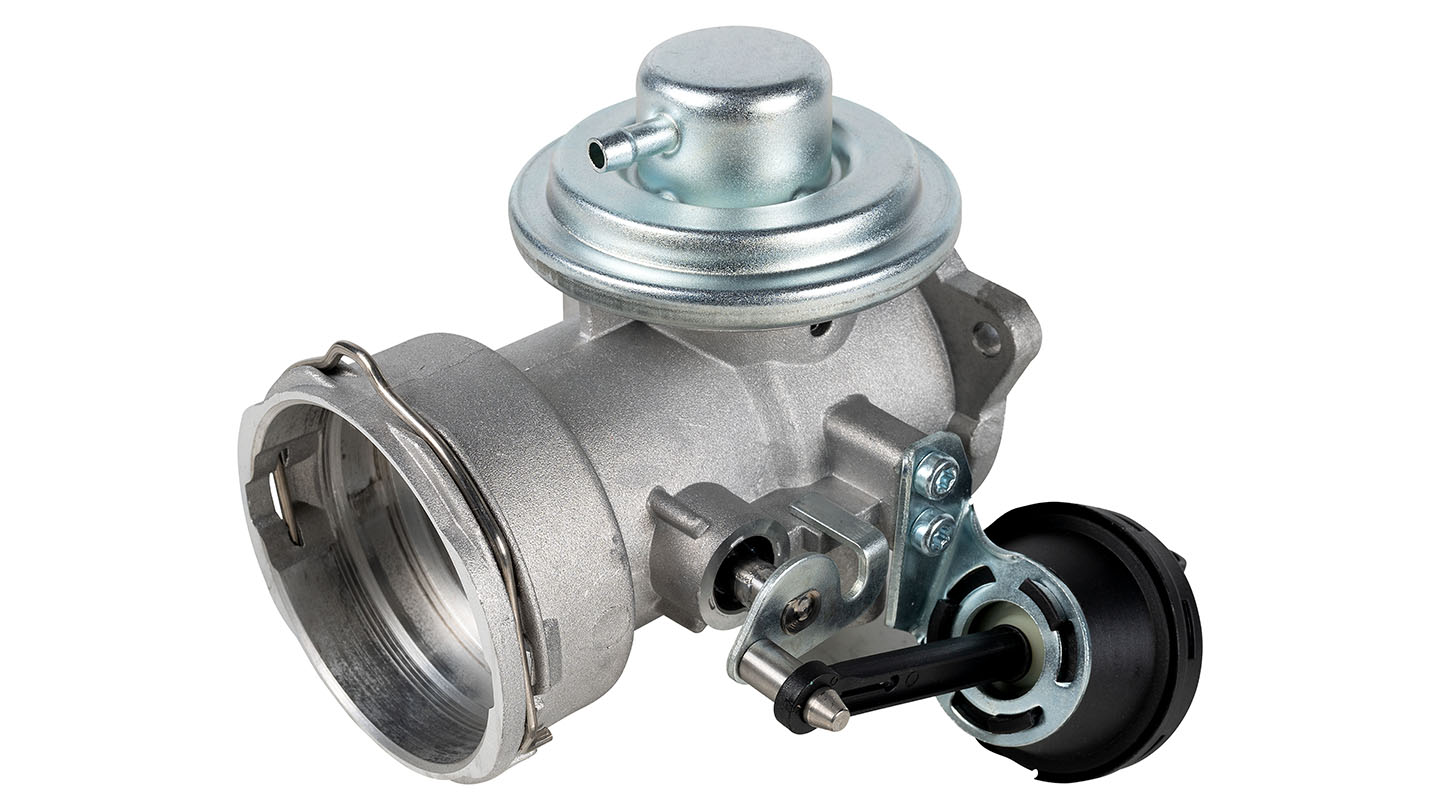

EGR valve appearance
EGR valves come in mechanical and electronic versions:
Both types are prone to malfunction, but the fixes differ: mechanical valves can often be cleaned, while electronic ones usually need to be replaced.
The EGR valve is typically positioned between the intake manifold and the exhaust manifold. Its core job is to recirculate a small amount of exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber. This process helps lower the combustion temperature, which in turn reduces the formation of NOx particles.
While especially important in diesel engines, the EGR system has been used since the 1970s—even in gasoline-powered vehicles in the U.S., where diesel usage has historically been low.
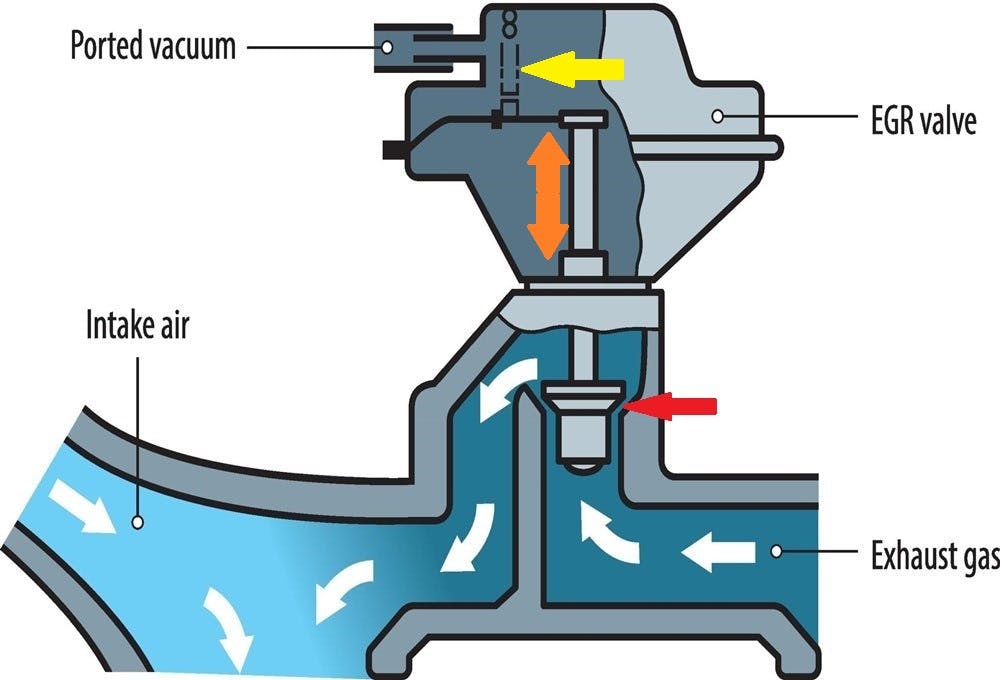
The EGR valve recirculates exhaust gas into the intake air to reduce engine emissions.
An electronic control unit (ECU) manages the EGR valve, opening and closing it based on key variables like engine load, RPM, throttle input, and temperature. For instance:
The general goal is to keep combustion temperatures as low as possible to reduce pollutant output.
Think of it like pouring hot tea: if you pour it from a high distance or pass it through several cups, it cools down. The EGR system "cools" exhaust gases by extending their journey and mixing them with fresh air before reentering the engine. The result is a cleaner, cooler burn.
So what happens when your EGR valve goes bad? Here are a few symptoms:
Most of these issues are caused by a valve that is stuck open or closed, or one that fails to regulate flow properly due to carbon deposits or electronic failure.

The EGR valve is clogged due to carbon deposits
This is where Autel diagnostic scanners come into play. With tools like the Autel MaxiSYS MS Ultra, or even the MK808Z/MK808S, you can:
Autel tools help you pinpoint the exact cause of the issue—whether it's a blocked passage, stuck valve, or electronic fault—saving you time and unnecessary repairs.
When the check engine light (especially that dreaded yellow engine icon) comes on, don’t ignore it—or worse, keep driving aggressively. In some cases, a simple scanner reset may solve the issue. In others, it could mean serious damage is on the way.
Autel scanners give you the power to diagnose early, act smart, and avoid costly surprises—making them a smart investment for any car owner or technician.